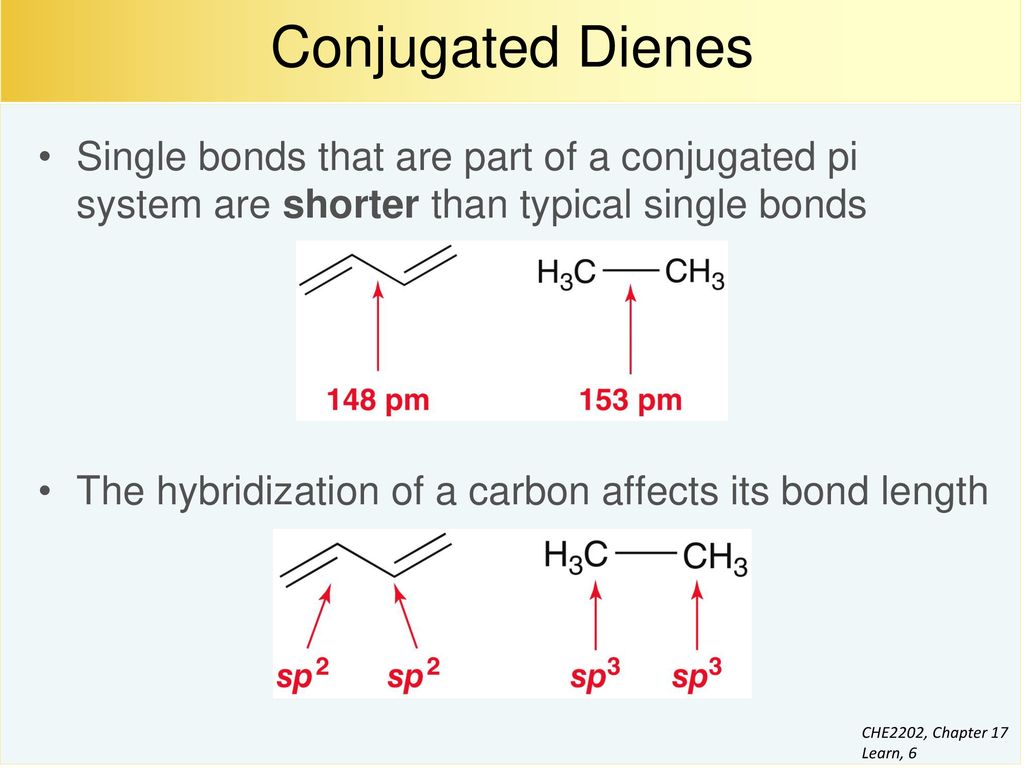
What Is A Conjugated System
What is a conjugated system. Conjugated carbonyls react with hydrogen cyanide to 14-keto-nitriles. The carbon at the center is abbreviated as a single dot. The Gilman reagent is an effective nucleophile for 14-additions to conjugated carbonyls.
Double bonds eg CC-CC-C in a molecule of an organic compound. Cumulated double bonds This molecule is known as allene containing two double bonds which share a carbon atom. It is this reflected portion that the eye will perceive as the color of that object.
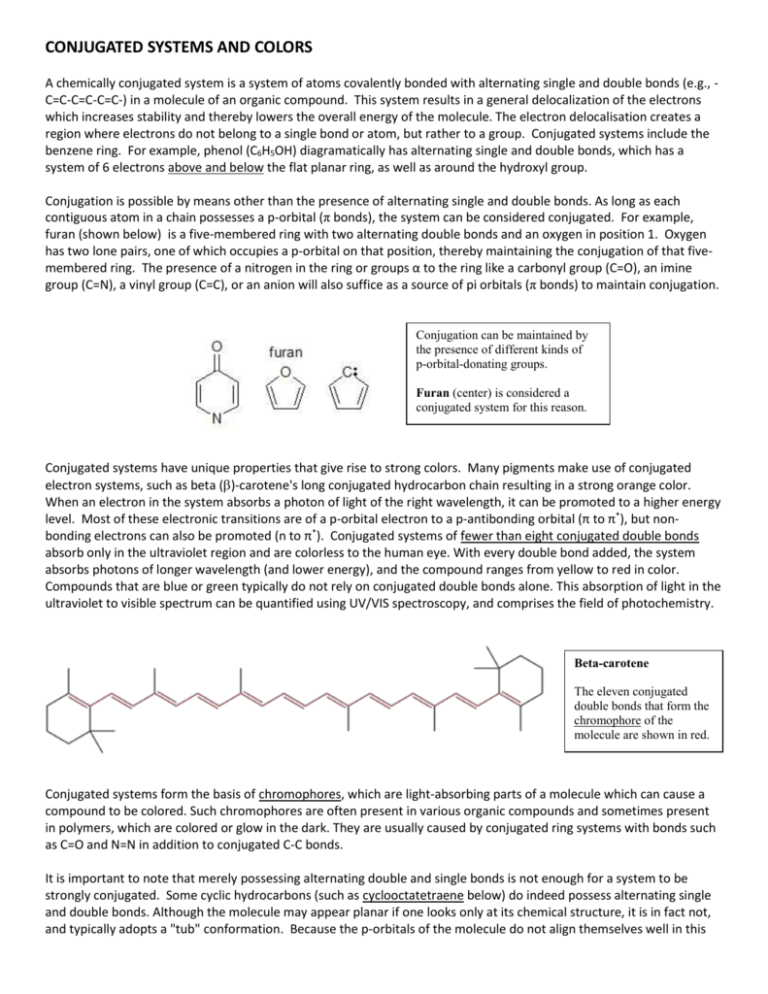
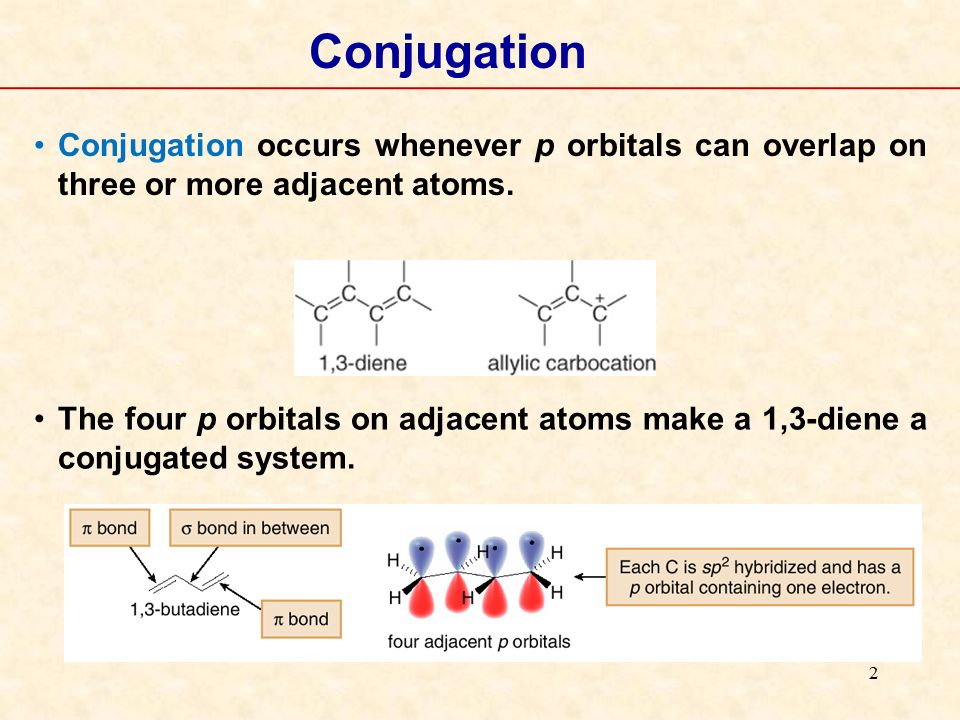
In chemistry a conjugated system is a system of connected p orbitals with delocalized electrons in a molecule which in general lowers the overall energy of the molecule and increases stability. Due to the conjugation the electrons can resonate between all conjugated p orbitals. One can think of conditioning on conjugate priors as defining a kind of discrete time dynamical system.
Learn faster with spaced repetition. Coordination Chemistry Reviews 2003. Conjugated systems of fewer than eight conjugated double bonds absorb only in the ultraviolet region and are colorless to the human eye.
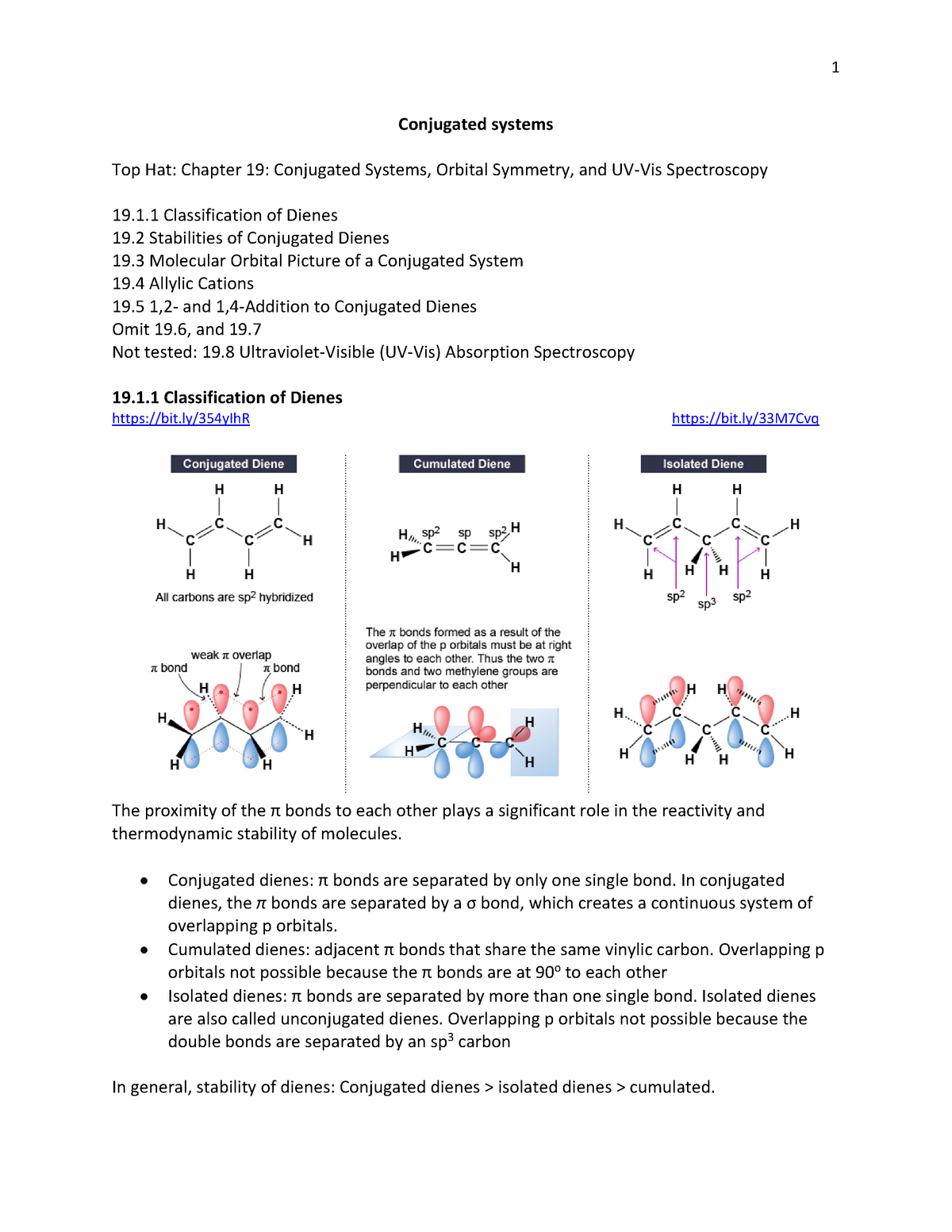
A conjugated system is a system of connected p-orbitals with delocalized electrons in compounds with alternating single and multiple bonds which in general may lower the overall energy of the. The main chain is conjugated and part of that same main chain is conjugated with the side group but all parts are not conjugated together as strongly. Conjugated polymers are materials in which a backbone of alternating single and multiple bonds result in π-conjugation by overlap of the π-orbitals giving rise to a continuum of energy states called a band structure.
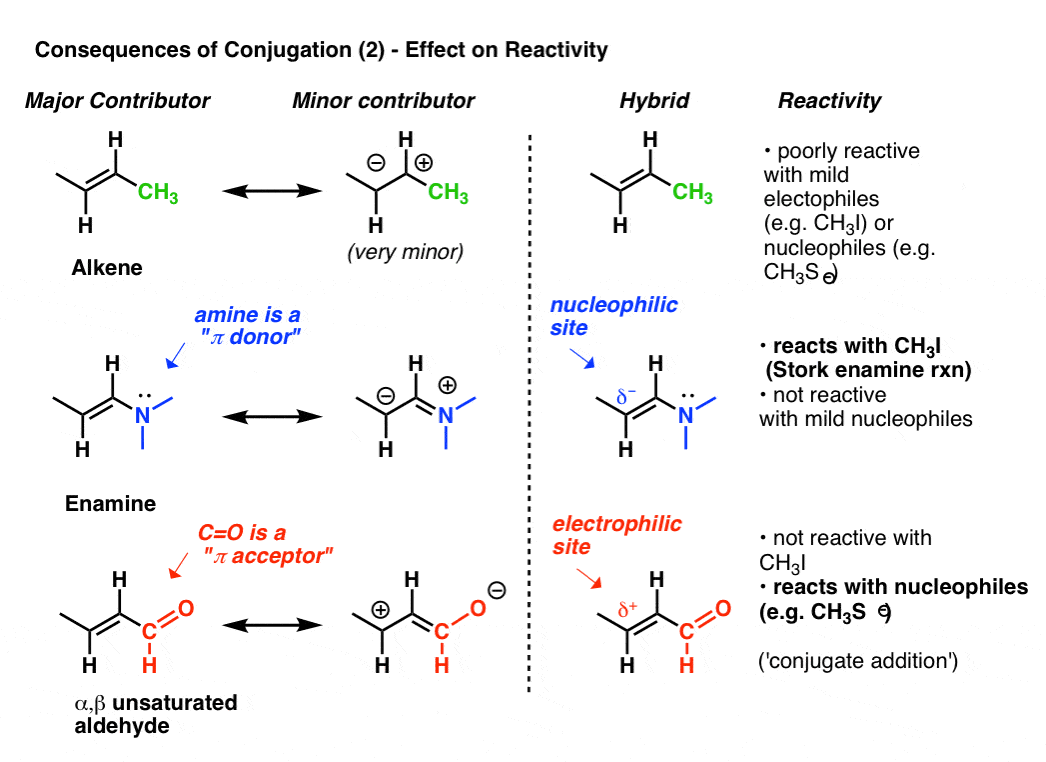
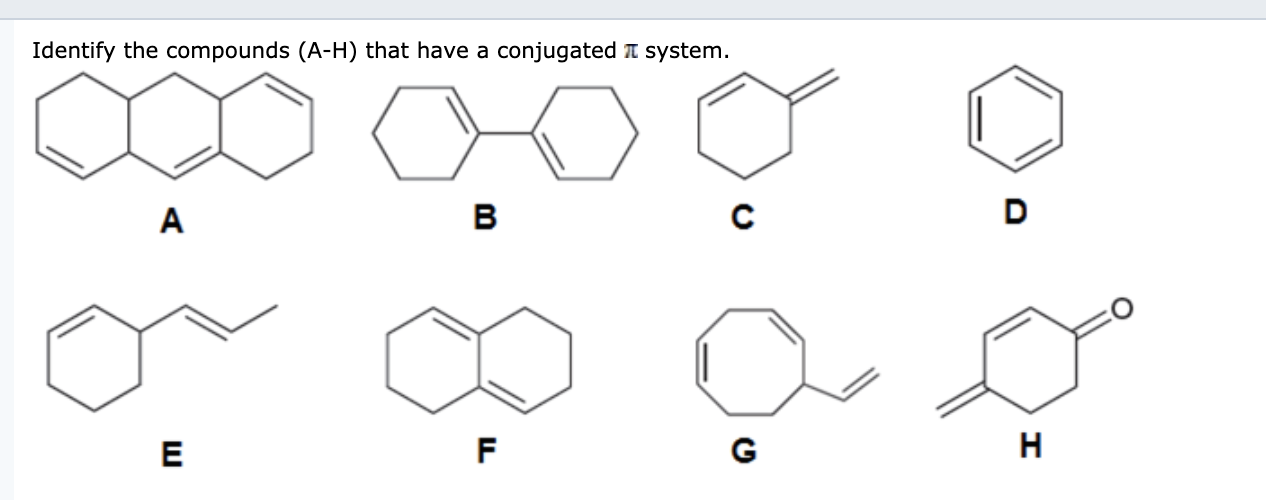
11 rows A conjugated system requires that there is a continuous array of p orbitals that can. A conjugated system is a type of a molecule where you have multiple p-orbitals interacting with each other. Conjugated carbonyls react with secondary amines to form 3-aminocarbonyls 3-ketoamines.
It can also be written as. Conjugated system then might absorb the lower energy portions of the light and reflect what is not absorbed.
Conjugated system in a covalent chemical compound a group or chain of atoms bearing valence electrons that are not engaged in single-bond formation and that modify the behaviour of each other.
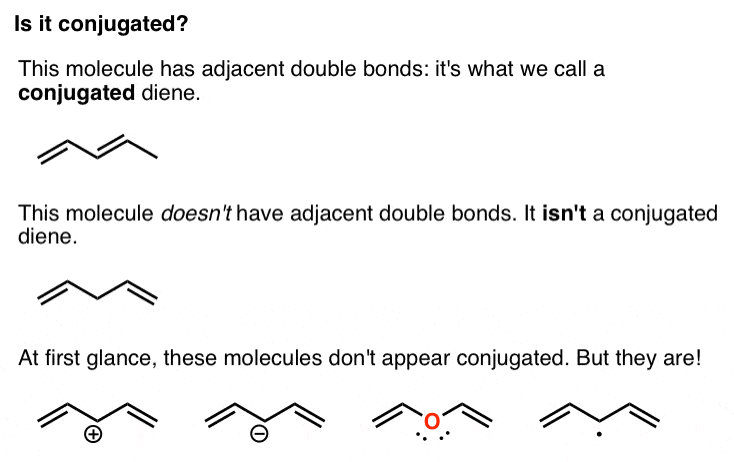
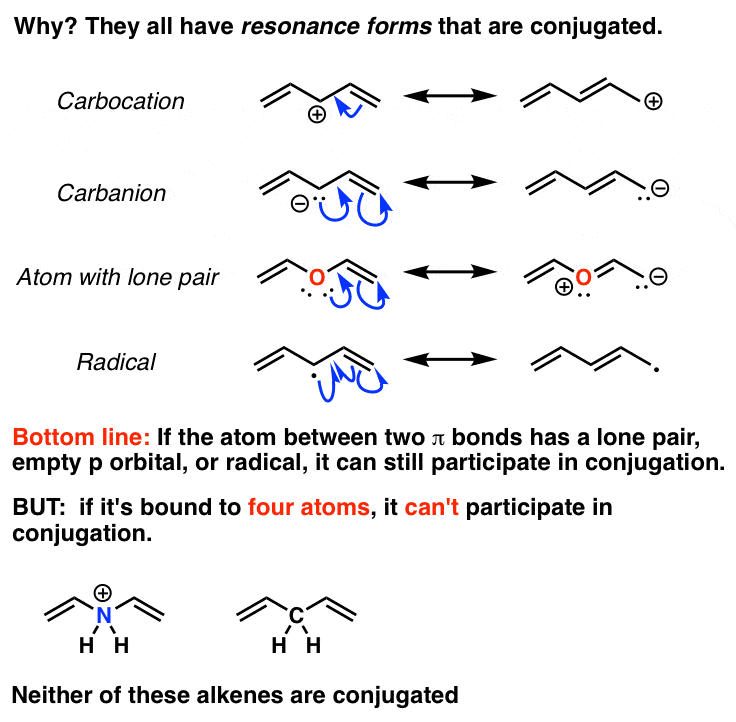
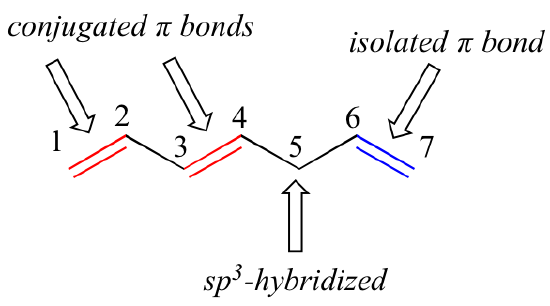
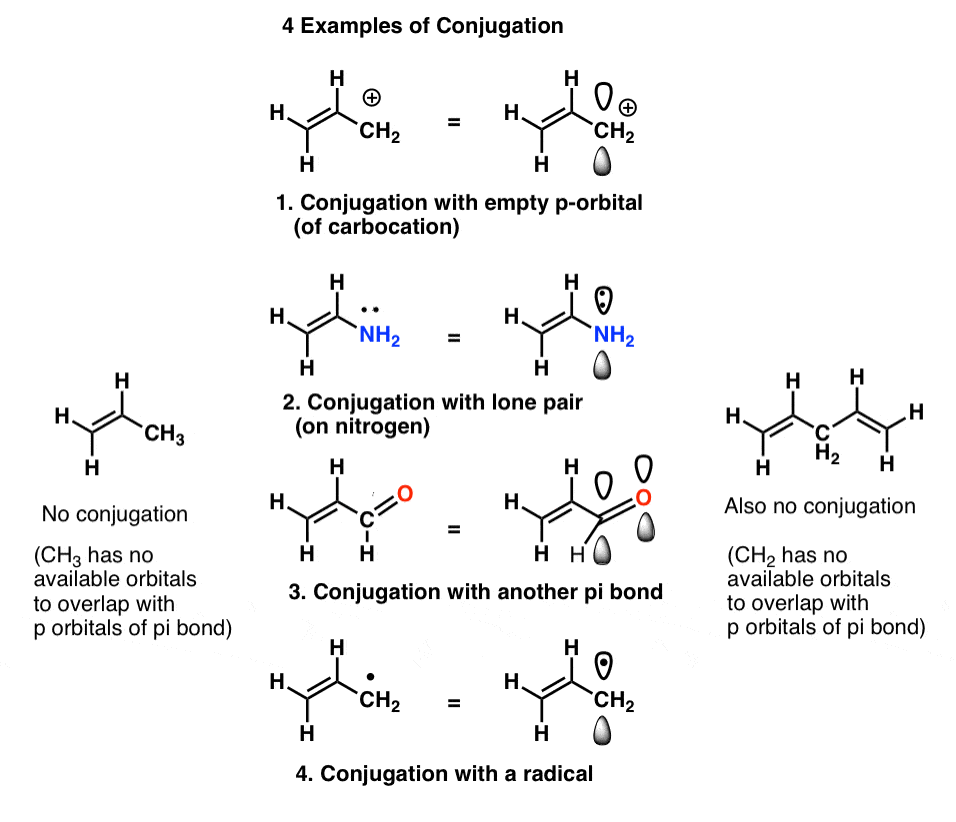
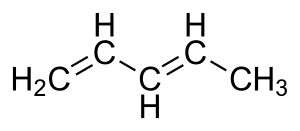
The carbon at the center is abbreviated as a single dot. Not only the pi bonds but also lone electron pairs radicals or carbenium ions can take part in creating a conjugated system. Introduction to allylic system. Since electrons are delocalized they belong to all the atoms in the conjugated system but not for only one atom. A conjugated system is a system of connected p-orbitals with delocalized electrons in compounds with alternating single and multiple bonds which in general may lower the overall energy of the. In classical terms one of the double-bonds branches off rather than continuing consecutively. If playback doesnt begin shortly try restarting your device. With every double bond added the system absorbs photons of longer wavelength and lower energy and the. This lowers the overall energy of the system and increase stability.
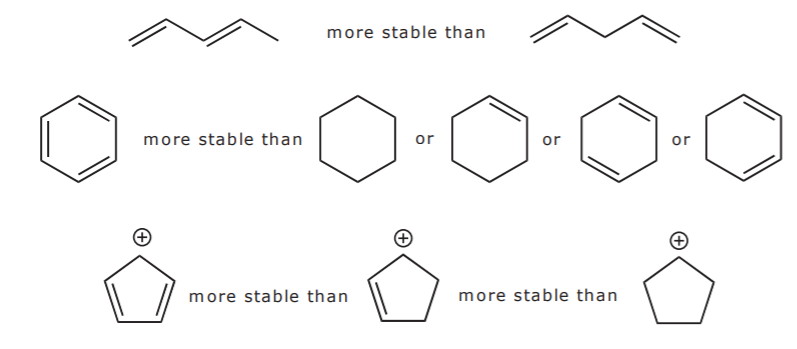
Asked Feb 12 in Biology Microbiology by gomichelle123. 11 rows A conjugated system requires that there is a continuous array of p orbitals that can. When the p orbitals of double bonds are on adjacent atoms. The conjugated system is thermodynamically more stable than non-conjugated system hence it is at lower energy. Study Colour by Design - Colour and Conjugated Systems flashcards from Charlie COLLIERs class online or in Brainscapes iPhone or Android app. Conjugated polymers are materials in which a backbone of alternating single and multiple bonds result in π-conjugation by overlap of the π-orbitals giving rise to a continuum of energy states called a band structure. The term conjugated double bond means that there is an alternative single and a double bond.






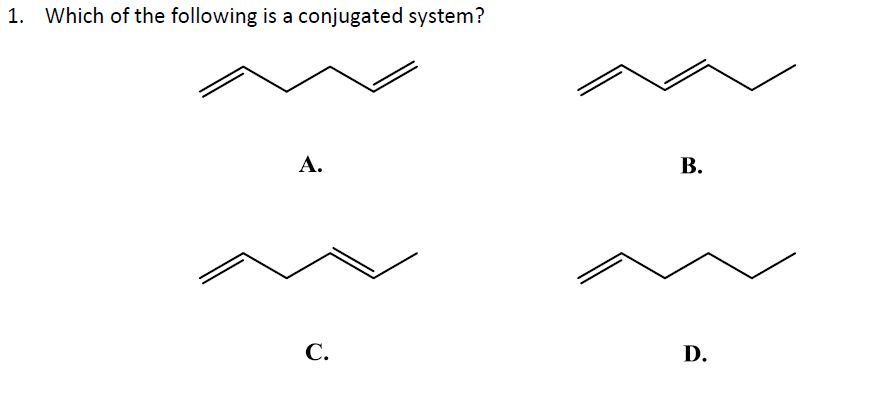
















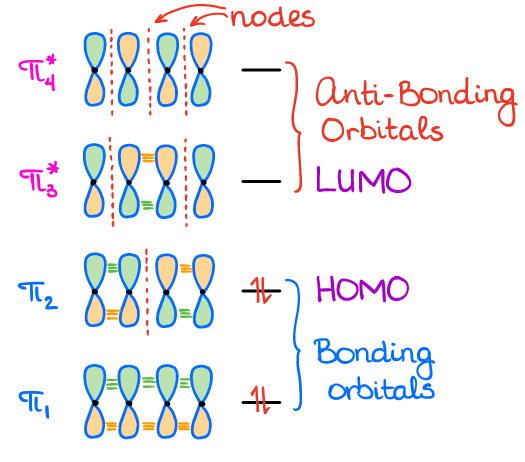


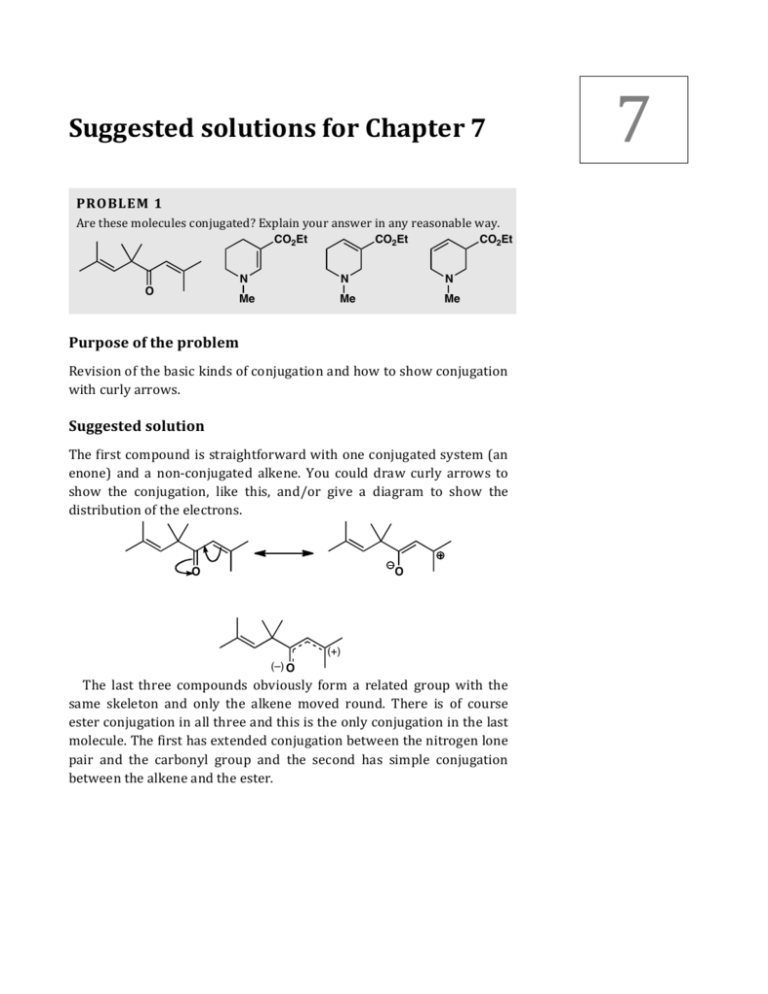


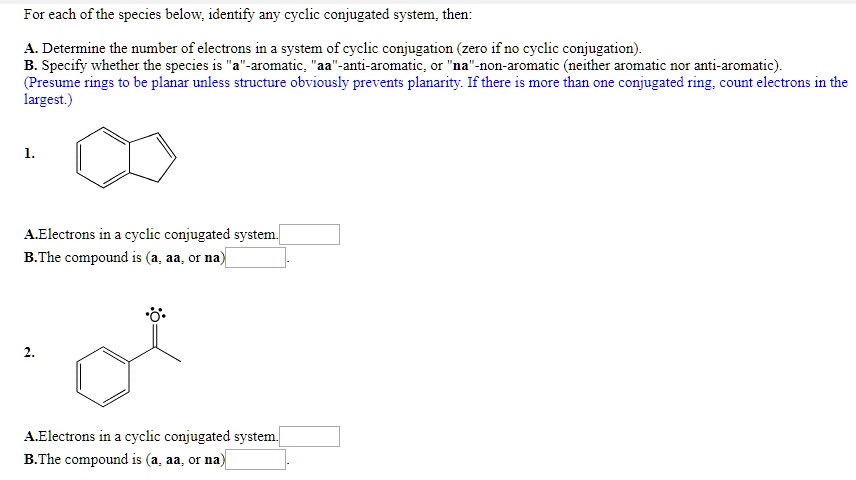


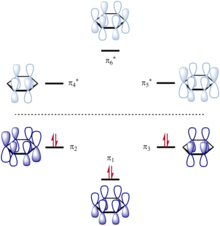
Post a Comment for "What Is A Conjugated System"